Baekjoon 1946
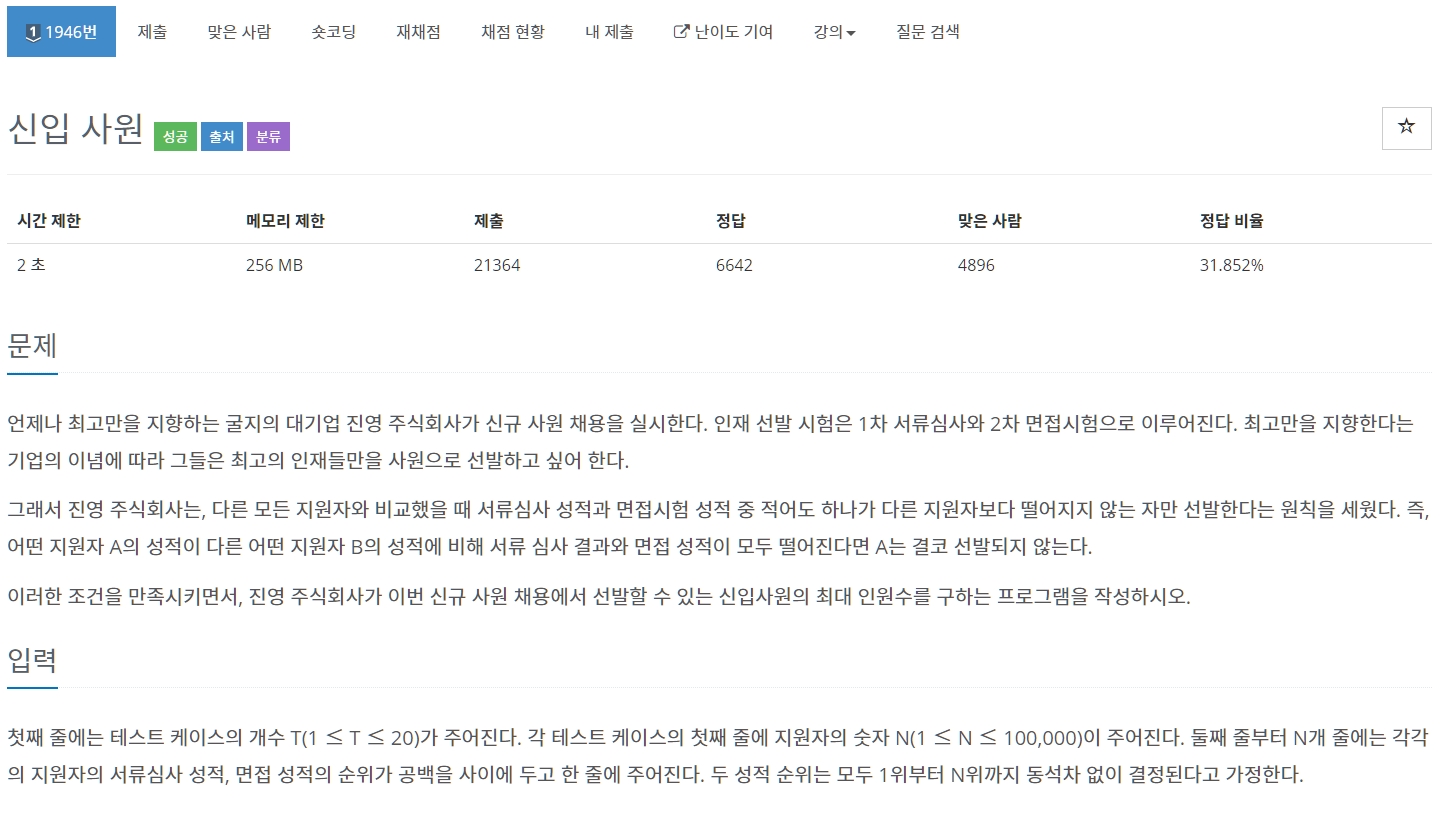
신입 사원
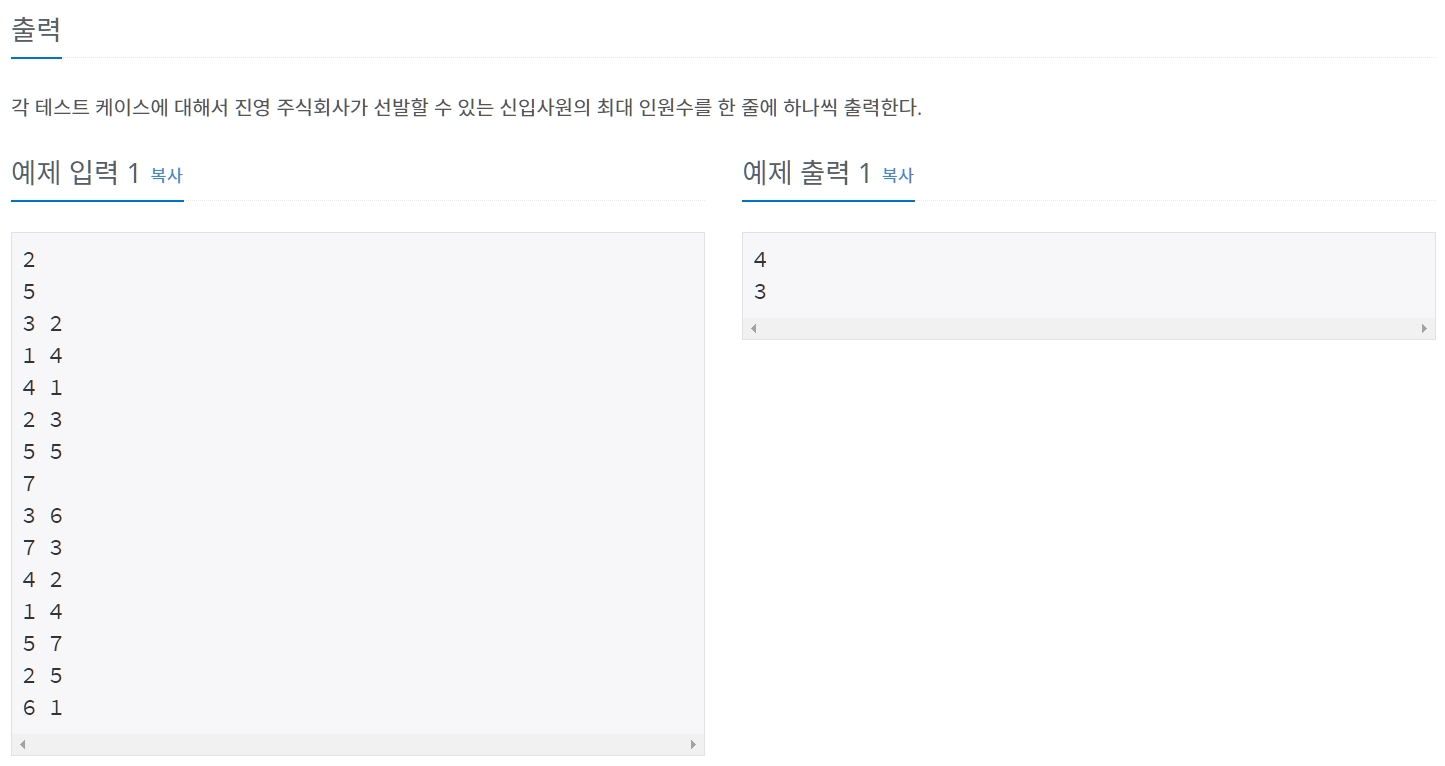
QUESTION ❔
CODE ⌨️
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class info
{
public:
int st;
int nd;
};
int T, N;
int a, b;
int maxcnt = 0;
int temp;
vector<int> answer;
bool cmp(info a, info b)
{
if (a.st == b.st)
{
return a.nd < b.nd;
}
else return a.st < b.st;
}
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> T;
for (int i = 0; i < T; i++)
{
cin >> N;
vector<info> vec;
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
cin >> a >> b;
vec.push_back({ a, b });
}
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), cmp);
temp = vec[0].nd;
maxcnt = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < vec.size(); i++)
{
if (vec[i].nd <= temp)
{
temp = vec[i].nd;
maxcnt++;
}
}
answer.push_back(maxcnt);
}
for (int i = 0; i < answer.size(); i++)
{
cout << answer[i] << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
RESULT 💛

SIMPLE DISCUSSION ✏️
Greedy 알고리즘 관련 문제였다. 새로운 아이디어를 공부할 수 있었다.
SOURCE 💎
Baekjoon_Link 👈 Click here
*****
NOT A TALENT ❎ NOT GIVING UP ✅
CopyRight ⓒ 2022 DCherish All Rights Reserved.
CopyRight ⓒ 2022 DCherish All Rights Reserved.