Baekjoon 3020
개똥벌레
QUESTION ❔
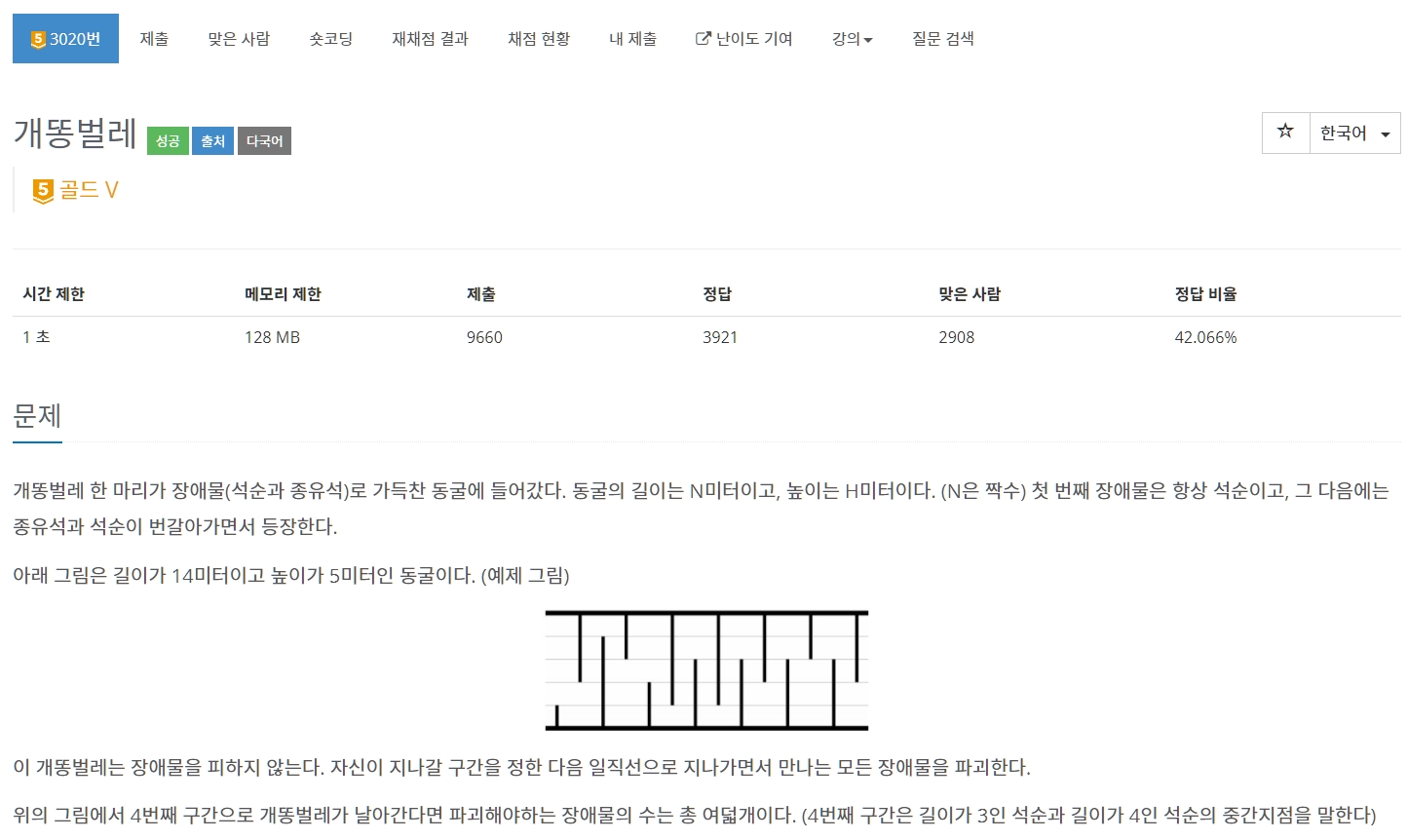
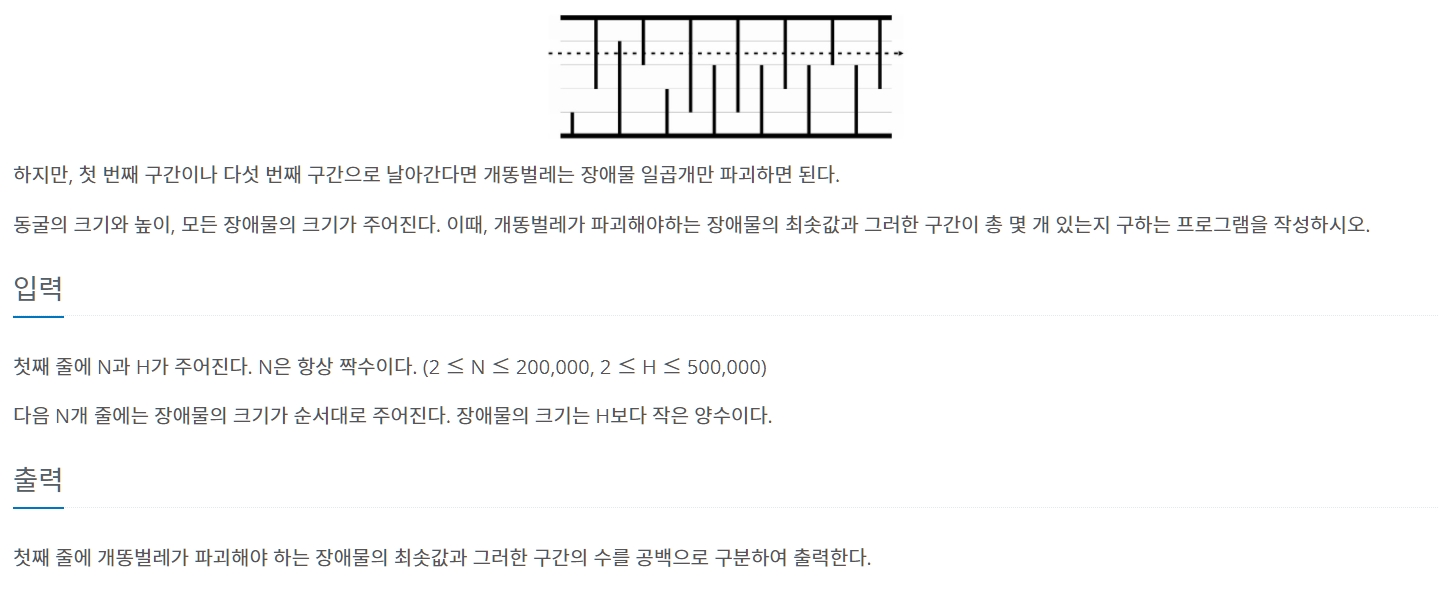
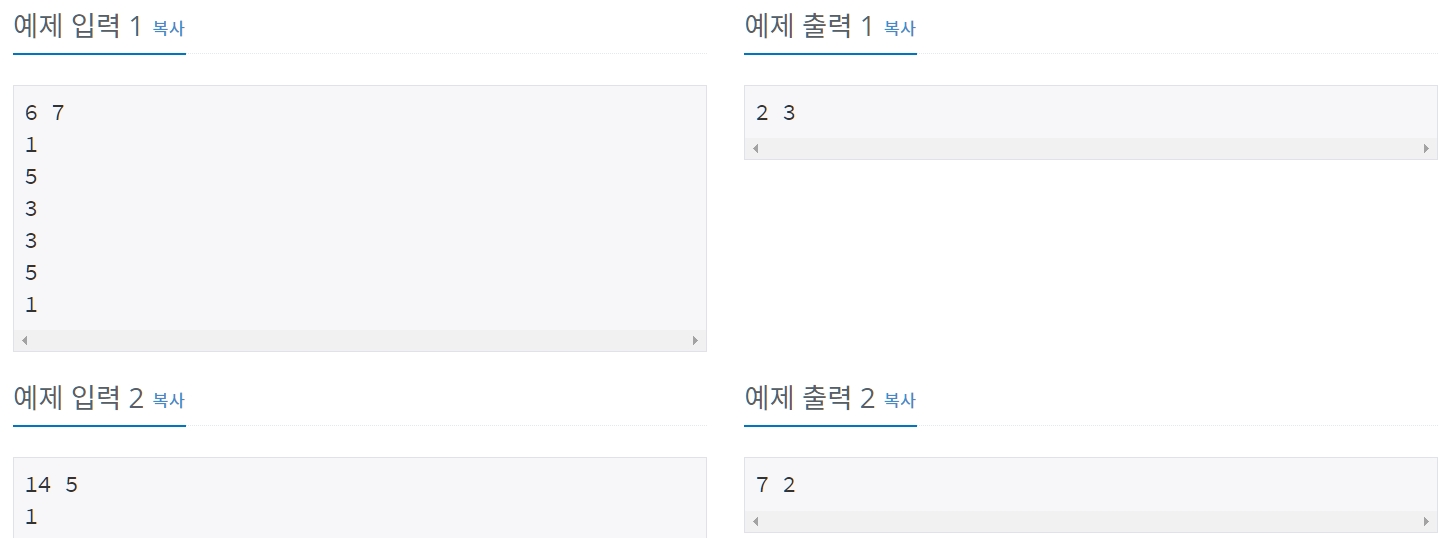
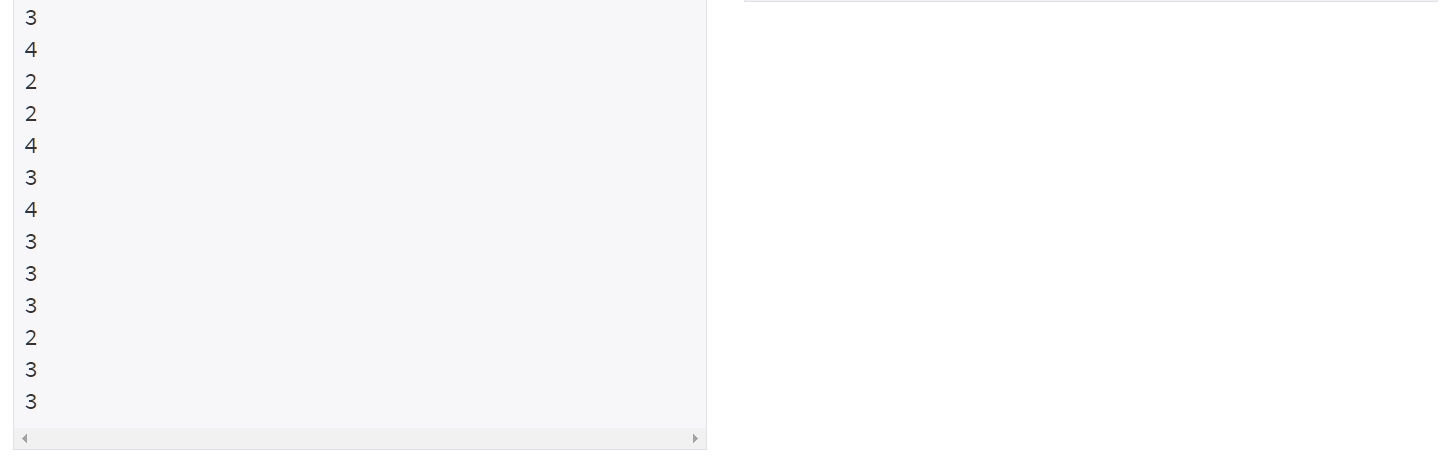
CODE (prefix_sum) ⌨️
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int N, H, d, u;
int idx, cnt;
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> N >> H;
idx = N;
cnt = 0;
vector<int> bottom(H + 1);
vector<int> top(H + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < N / 2; i++)
{
cin >> d >> u;
bottom[d] += 1;
top[u] += 1;
}
for (int i = H - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
bottom[i] += bottom[i + 1];
top[i] += top[i + 1];
}
for (int i = 1; i < H + 1; i++)
{
if (idx > bottom[i] + top[H - i + 1])
{
idx = bottom[i] + top[H - i + 1];
cnt = 1;
}
else if (idx == bottom[i] + top[H - i + 1])
{
cnt++;
}
}
cout << idx << " " << cnt << "\n";
return 0;
}
CODE (binarysearch) ⌨️
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int N, H;
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> N >> H;
vector<int> bottom(N / 2);
vector<int> top(N / 2);
for (int i = 0; i < N / 2; i++)
{
cin >> bottom[i] >> top[i];
}
sort(bottom.begin(), bottom.end(), less<int>());
sort(top.begin(), top.end(), less<int>());
int result = N;
int cnt = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= H; i++)
{
int temp = bottom.size() - (lower_bound(bottom.begin(), bottom.end(), i) - bottom.begin());
temp += top.size() - (upper_bound(top.begin(), top.end(), H - i) - top.begin());
if (result == temp) cnt++;
else if (result > temp)
{
result = temp;
cnt = 1;
}
}
cout << result << " " << cnt << "\n";
return 0;
}
RESULT 💛

SIMPLE DISCUSSION ✏️
수학 관련 문제였다. 누적 합 혹은 이분 탐색을 이용하여 문제를 해결할 수 있었다.
RESULT 💛

SIMPLE DISCUSSION ✏️
수학 관련 문제였다. 누적 합 혹은 이분 탐색을 이용하여 문제를 해결할 수 있었다.
SOURCE 💎
Baekjoon_Link 👈 Click here
*****
NOT A TALENT ❎ NOT GIVING UP ✅
CopyRight ⓒ 2022 DCherish All Rights Reserved.
CopyRight ⓒ 2022 DCherish All Rights Reserved.